Reciprocal Gait Pattern
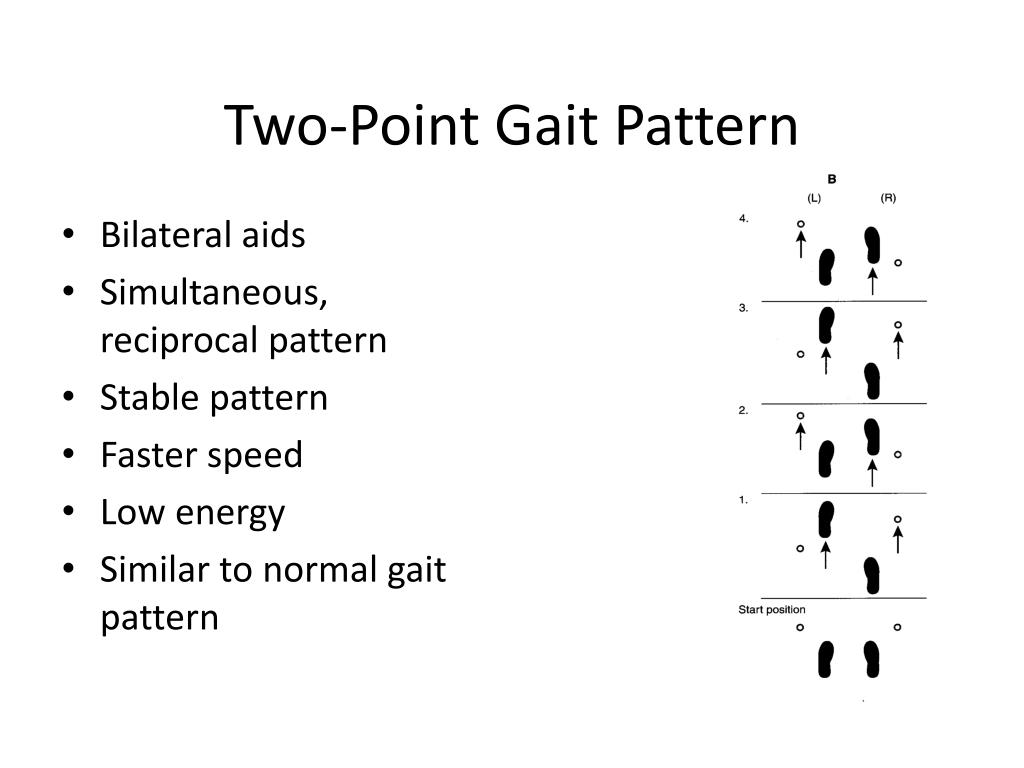
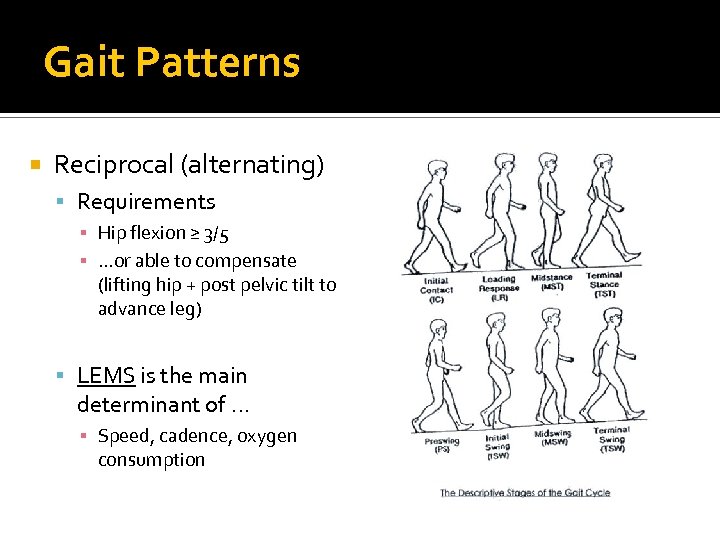
Reciprocal Gait Pattern - Walking with partial paralysis of the lower limbs. Heel strike appears by 1 1/2 years. Web when the muscles that lift the foot are paretic the patient must lift the leg higher than usual during the swing phase. Web gait is a term used to describe a walking pattern. It is meant to assist those with paralysis of the lower trunk, hips. Web between 1 and 3 years, certain observational determinants appear in a child's gait pattern: Web understanding the gait cycle allows for effective gait analysis. Effective evaluation of a patient s gait requires a systematic approach to the observation of the gait. Obliquity, hip adduction/abduction, and possibly rotation, the patient. Certain gait abnormalities are temporary and others require lifelong management. Sometimes, an injury or underlying medical condition can cause an abnormal gait. The recovery or improvement of ambulation after a spinal cord injury (sci) is an important goal because people who can walk independently are more likely to be able to participate in expected social roles and desired recreational activities, have a higher quality of life, and have improved health status. An rgo allows the user to create reciprocal (forward and backward) movement of the legs, and to regulate their gait while walking. Standing and walking with lower limb paralysis. Web gait assessment describes the patterns of movement that control the progression of the body in walking. Web stairs reciprocal gait (stair training, full weightbearing, reciprocal gait) stand at the bottom of the stairs. Characterized by a shorter step length and stance time on the side of the painful lower extremity. Bring one leg onto the first step. Has no reciprocal arm swing and displays a high guard. reciprocal arm swing present in 65% by 1 1/2 yrs, in 92% by 2 yrs, in 98% by 3 1/2 yrs, in all by 4 yrs. Long unobstructed hallway with low traffic. Characterized by a shorter step length and stance time on the side of the painful lower extremity. Obliquity, hip adduction/abduction, and possibly rotation, the patient. Walking with partial paralysis of the lower limbs. The recovery or improvement of ambulation after a spinal cord injury (sci) is an important goal because people who can walk independently are more likely to be. Bipedal gait requires a combination of automatic and volitional postural components. Web a reciprocating gait orthosis (rgo) is a type of hkafo that enables a reciprocating gait pattern. You may notice an abnormal gait if you drag your toes when you walk, take high steps or feel off balance when walking. Stride is a whole gait cycle. Should be asked. Characterized by a shorter step length and stance time on the side of the painful lower extremity. Long unobstructed hallway with low traffic. It is meant to assist those with paralysis of the lower trunk, hips. Obliquity, hip adduction/abduction, and possibly rotation, the patient. Web there are eight basic pathological gaits that can be attributed to neurological conditions: Parkinson’s disease may affect these patterns. Web stairs reciprocal gait (stair training, full weightbearing, reciprocal gait) stand at the bottom of the stairs. Sometimes, an injury or underlying medical condition can cause an abnormal gait. Take your starting leg up to the third step. Effective evaluation of a patient s gait requires a systematic approach to the observation of the. Effective evaluation of a patient s gait requires a systematic approach to the observation of the gait. Take your starting leg up to the third step. It is meant to assist those with paralysis of the lower trunk, hips. Standing and walking with lower limb paralysis. Has no reciprocal arm swing and displays a high guard. reciprocal arm swing present. A single cycle of gait starts when the heel of one foot strikes the ground and ends when that same heel touches the ground again. Hemiplegic, spastic diplegic, neuropathic, myopathic, parkinsonian, choreiform, ataxic (cerebellar) and sensory. Bring one leg onto the first step. Parkinson’s disease may affect these patterns. Web gait cycle is a repetitive pattern involving steps and strides. When analysing gait, it should be done systematically, looking at each joint separately throughout the entire gait cycle and detecting deviations from normal. Patients are unable to stand or walk on their heels. If there is a rail hold onto it with one hand. The recovery or improvement of ambulation after a spinal cord injury (sci) is an important goal. It may be accompanied by ipsilateral trunk lean with hip pain or. If there is a rail hold onto it with one hand. Standing and walking with lower limb paralysis. Walking with partial paralysis of the lower limbs. You may notice an abnormal gait if you drag your toes when you walk, take high steps or feel off balance when. Long unobstructed hallway with low traffic. Web how do i do it? Hemiplegic, spastic diplegic, neuropathic, myopathic, parkinsonian, choreiform, ataxic (cerebellar) and sensory. An rgo can be used to treat people with paralysis due to spinal cord injury or other neurological diseases including spina bifida. Characterized by a shorter step length and stance time on the side of the painful. Parkinson’s disease may affect these patterns. The resulting gait pattern is referred to as steppage gait. Obliquity, hip adduction/abduction, and possibly rotation, the patient. Take the other leg onto the second step. Peroneal splints and orthopedic footwear are usually helpful. Make sure you can see the knee caps and feet. Characterized by a shorter step length and stance time on the side of the painful lower extremity. The resulting gait pattern is referred to as steppage gait. Web subscribe now to access 400+ patient education videos and handouts: Web the gait cycle describes the cyclic pattern of movement that occurs while walking. Web between 1 and 3 years, certain observational determinants appear in a child's gait pattern: Web a reciprocating gait orthosis (rgo) is a type of hkafo that enables a reciprocating gait pattern. Sometimes, an injury or underlying medical condition can cause an abnormal gait. Heel strike appears by 1 1/2 years. Web understanding the gait cycle allows for effective gait analysis. It controls hip extension and assists with. Has no reciprocal arm swing and displays a high guard. reciprocal arm swing present in 65% by 1 1/2 yrs, in 92% by 2 yrs, in 98% by 3 1/2 yrs, in all by 4 yrs. Take your starting leg up to the third step. Certain gait abnormalities are temporary and others require lifelong management. With an rgo, one leg can pass in front of the other, creating a more typical pelvic rotation. An rgo can be used to treat people with paralysis due to spinal cord injury or other neurological diseases including spina bifida.Reciprocating gait arthosis
Reciprocating Gait Orthosis
PPT Ambulation Aids Normal Gait and Abnormal Gait PowerPoint
Typical gait cycle is shown with isocentric reciprocating gait orthosis
Reciprocal Gait Pattern YouTube
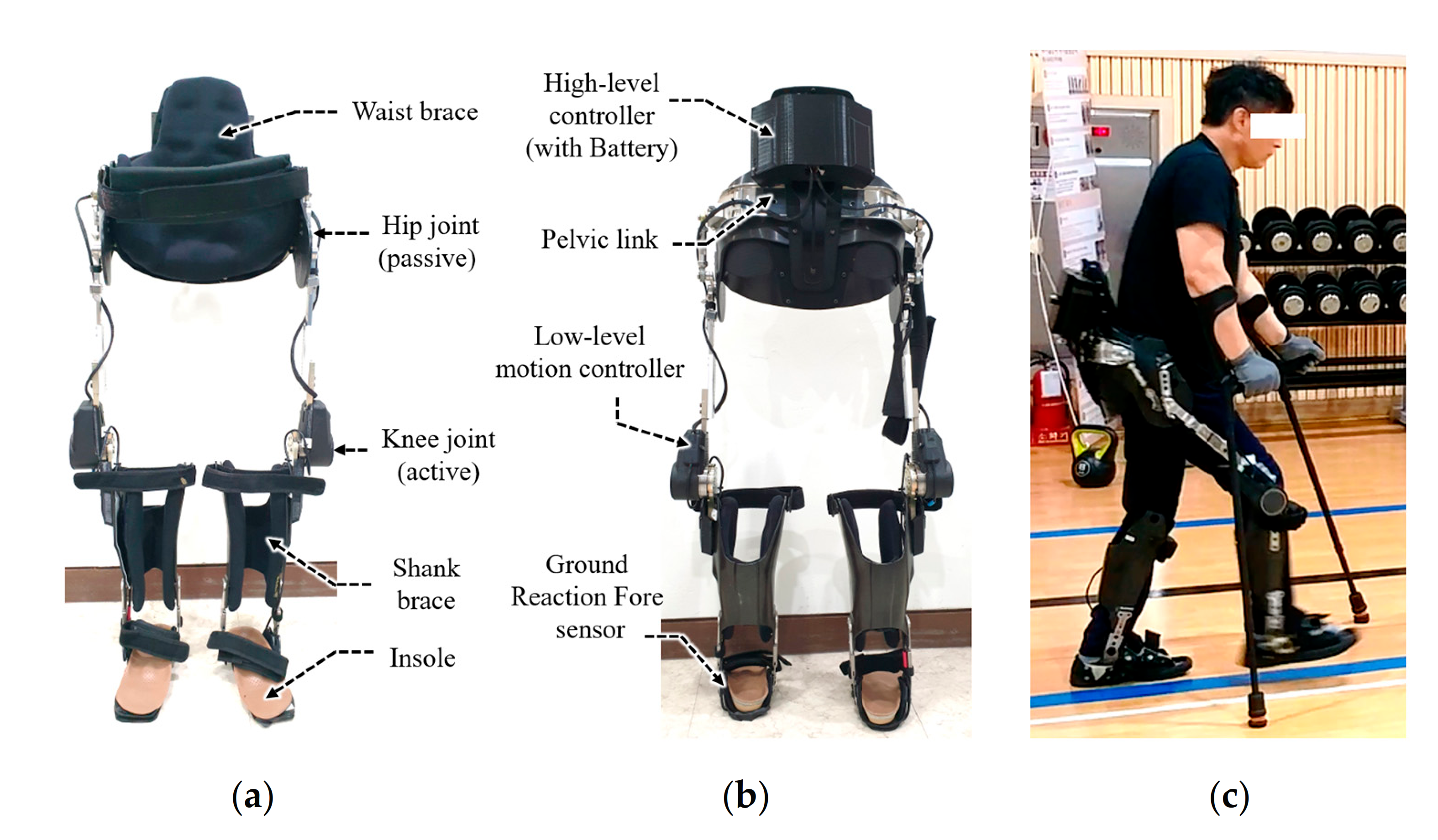
The advanced reciprocal gait orthoses used in this study. (a) ARGO with
Reciprocal Gait With Fourwheel Walker MedBridge YouTube
4 Pt Gait Reciprocal YouTube
Ambulation after SCI Dr Jeff Tubbs 4 16 14
Reciprocating gait orthosis (RGO) (a) Frontal view (b) Side view
Effective Evaluation Of A Patient S Gait Requires A Systematic Approach To The Observation Of The Gait.
It May Be Accompanied By Ipsilateral Trunk Lean With Hip Pain Or.
It Is Meant To Assist Those With Paralysis Of The Lower Trunk, Hips.
Web There Are Eight Basic Pathological Gaits That Can Be Attributed To Neurological Conditions:
Related Post: